Food Animal Male Urogenital Surgery
Preputial surgery
Many preputial wounds will need eventual surgery. This may be sharp debridement and primary closure but more often this is reconstructive surgery. There are two main options for preputial reconstruction : reefing (circumcision) and amputation. These surgeries are essentially the same as rectal prolapse surgery; reefing is essentially submucosal resection while amputation is similar in both. Vaginoplasty would also equate to reefing.
Preputial resection
Preputial resection is preferred over preputial amputation when possible. It is only possible when the penis can be extended and exteriorized. With the penis extended, the damaged area of prepuce is removed by making a circumferential incision around each side of the damage. These are connected by a longitudinal incision and then peeled off the underlying layers. The two circumferential incisions are then reanastomosed, taking care to not twist the penis and prepuce while doing so.
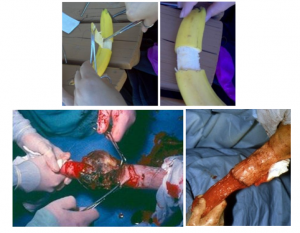
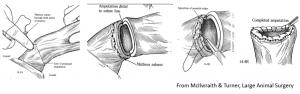
Preputial amputation
Preputial amputation is performed when the penis cannot be exteriorized. After placement of overlapping sutures 360º around the healthy prepuce to control bleeding, the distal prepuce is transected and the cut edges anastomosed. It may be helpful to cut a “v” incision in to the circle to avoid cicatrix formation. These do tend to stricture, regardless. For breeding purposes, a prepuce length of at least 1.5-2x as long as the free portion of the penis.
Resources (google at your own risk)
How to- preputial resection chapter
Medical and Surgical Management of Conditions of the Penis and Prepuce, 2024 VCNA
Penile and preputial problems in the bull, MS Gill
Surgical procedures in the bovine, start at page 13

