Equine and Camelid Castration
Equine Castration Overview
Overview
Most adult horses are castrated. This minimizes the dangers and decreases the number of unexpected pregnancies. Stallions can be ridden and trained but do need special housing, care, and handling. Geldings are easier to manage. Most colts are castrated between 6 months and 2 years of age; many practitioners aim for 1-1.5 years of age.
Testosterone is responsible for the male sexual characteristics in horses, including the muscular jaw, neck and body. Testosterone also stimulates growth plate closure. Animals that are castrated earlier in life may develop longer and straighter limbs and grow taller because they grow for a longer period of time. Horses castrated too early may actually develop orthopedic issues (arthritis) due to the straighter limb conformation. Research results are contradictory on this topic.
Younger horses can be very challenging to castrate as the smaller testicles are very mobile and are often not found in the scrotum and/or are hard to keep in the scrotum. Smaller testicles are also more easily confused with other structures (including the penis).
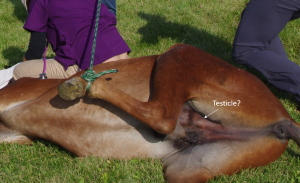
The castration procedure is usually done on the farm where the colt lives. Supplies are generally only those brought with you on your truck. Due to variability in horse responses to handing and anesthesia as well as to challenges of working outside, make sure your truck is stocked with double what you anticipate needing!
Castration steps
The following is a rough outline of the process. Please refer to the following chapters for more details.
Ensure the colt is healthy, manageable and has two testicles
Castration is an elective procedure. The horse should be vaccinated (especially for tetanus) and not be showing any signs of illness. The day of castration is not a time to halter break a colt if there are any alternatives. It is very nice to know how much the horse has been handled and his response to handling. Yes, he has a halter on but does he actually respond to signals?
Do a thorough examination including palpation of the testicles if possible. Be sure and listen to the heart!

Horses are rarely monorchid but can have delayed or inhibited testicular descent (cryptorchidism). It is imperative that either both or no testicles are removed. Leaving one testicle for a later procedure is considered both unethical and unwise. The horse appears to be a gelding but can act like a stallion. Records are not usually reliable enough to ensure a perfect testicle-finding-surgical approach at a later date and records can be separated from the horse. Do not remove a lone testicle. If you think you have two testicles, remove the less obvious one first. You can always stop and wake the horse up if it is not truly a testicle.
If you can avoid fly season, that is ideal.
Decide on recumbent or standing castration, location, and roles
Most surgeons have a preference for either recumbent or standing castration. Both work. Sometimes a situation or a horse’s characteristics means one is a better option.
A grassy field away from cars, roads, buildings and other animals is best. Stalls are dangerous (minimal escape routes for you and it is easy for the horse to get injured if it flops around). Sand gets into everything and mud contains infection potentiating factors. If a horse can run into a tree or roll under a fence, it will.
Your client should play a minimal role; use your technician, vet student or prevet student for any horse handling.

Administer preoperative medications
Horses should receive an NSAID preoperatively. Antibiotics do reduce the risk of postoperative complications but are not required. Tetanus vaccination should be up to date (within 6 months) or boostered. Remember, the first tetanus toxoid takes a couple of weeks to provide a full response. Tetanus antitoxin can be used to provide an earlier immune response but antitoxin has been associated with serum hepatitis and equine parvovirus infection. If the horse is unvaccinated, it is better to vaccinate with tetanus toxoid and wait to castrate, if possible. This avoids the risk of tetanus antitoxin.
Place an iv catheter if desired (this a good idea unless you have a donkey or a miniature stallion – sometimes getting a catheter in those isn’t worth the effort).
Sedate or anesthetize the horse
This includes placing a local block in the testicle or spermatic cord. It is done carefully in the standing castration and after the horse is recumbent for recumbent castrations.

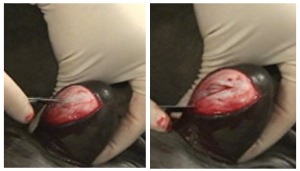
Castrate the horse
Castration may be performed via an open or closed method, depending on whether the vaginal tunic is cut to expose the testicle (open) or removed with the testicle (closed). [Modified open/modified closed techniques have been shown to have more complications.] In most cases, an incision is made over each testicle. After the testicular artery is ligated, crushed and/or twisted to create hemostasis, each testicle is removed. The incisions are left open for drainage; they are usually stretched to make sure they are well open! Before the horse wakes up, other procedures may be performed such as hoof trimming or wolf tooth extraction.
Recover the horse
The horse is allowed to stand on its own time (if recumbent) and returned to its stall once able to walk safely.

Educate the client on postoperative care
Most horses are stall rested for the remainder of the day. The colt can be fed once he is fully awake. After the first day, the colt should be exercised to keep the surgical site open and draining. Too much swelling will cause the incision to seal together and prevent that drainage. If not draining, the area can readily become swollen and/or infected. NSAIDs help decrease swelling and encourage exercise. A horse turned out on its own and in pain is unlikely to exercise.
Horses may retain stallion-like behavior even after the testicles are removed; however, most lose the behavior after a few days or weeks. New geldings can remain fertile for several weeks (it depends on if they have viable sperm in the epididymis at castration and if they ejaculate or not). New geldings should be separated from mares for at least two days; many recommend two months to be totally safe.
Resources
This video gives a general overview of the process (4 min)
Castration in the horse, The Horse, 2001 – nice overview written for clients
Castration complications: A review of castration techniques and how to manage complications. VCNA (2021): 37:259-273
-
- Note- Please continue NSAIDs for 3 days postoperatively and most horses that develop infections due to premature scrotal closure do not need antibiotics, just drainage.

