Equine tendons and ligaments
Tendon laxity
In premature and neonatal foals, tendons and ligaments may be too relaxed instead of too contracted. As weight bearing is not always balanced, this can lead to abnormal limb and foot angulation. The foal may tip back on its heel with an elevated toe. This is not a deep flexor tendon injury but is too much tendon stretch.
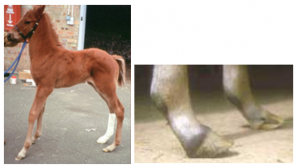
The foal may have angular limb deformities due to lack of joint control by weak ligaments. Often these are the “windswept” foals (look like the wind is blowing hard from one direction). In this foal, the left hock is varus while the right is valgus.

Tendons and ligaments strengthen as the foal matures and exercises lightly. Meanwhile it is imperative that foals not overexercise as abnormal forces on the physes could lead to secondary problems.
Bandaging is often attempted to “support” the limb. Due to the relaxation response seen in babies, this actually makes it worse. Our young animals have a weird muscle/tendon/ligament relaxation response when the limb is supported by bandaging, splinting or casting. This would make the limb functionally longer since the supporting structures stop supporting and are relaxed. Heel drops and toe goes up. Band-aids (light bandages) can be applied to prevent trauma on flooring but heavy wraps should be avoided. Tongue depressors or similar structures can be glued to the foot to help minimize weight shifts backwards.
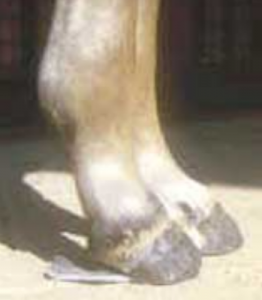
The prognosis is good if the rest of the foal is mature. It is always good to radiograph the cuboidal bones before exercising the baby (see angular limb deformities).
Key Takeaways
Tendon laxity is a sign of immaturity. Mild exercise should help strengthen the tendons. Avoid heavy bandages!
If the cuboidal bones are normal, these carry a good prognosis. Incompletely ossified cuboidal bones can lead to angular limb deformities.
Types of crooked legs in foals, UMN extension

