Bovine Lameness and Podiatry
Bovine Foot Anatomy
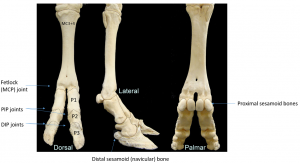
Bones and joints
While the cannon bone of a horse is MCIII or MTIII, in a cow it is a fused MCIII+IV or MTIII+IV. The fusion is present at the fetlock joint and above. Cattle do have the same bones and joints as horses below the fetlock but in duplicate form. There are four proximal sesamoid bones and two distal sesamoid bones on each limb. The fetlock joint is fused; the pastern and coffin joints are bilateral on each limb and separate.
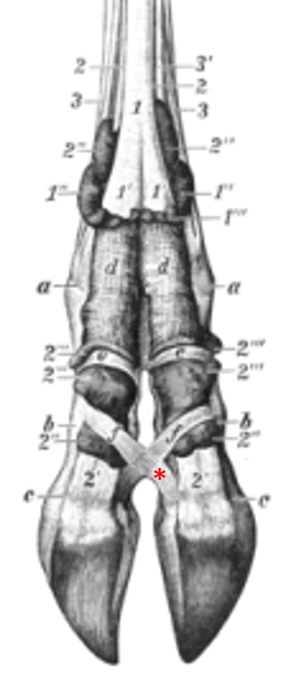
Interdigital ligaments keep the digits from splaying apart.
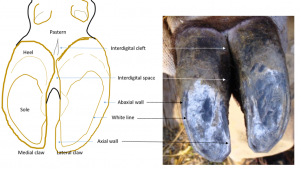
Foot structure

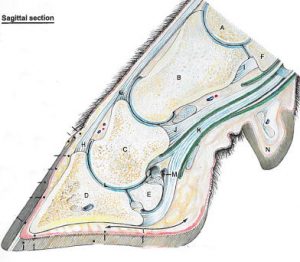
Flexor tuberosity
The deep flexor tendon attaches on the bottom of P3 at the flexor tuberosity. The pressure of this tuberosity creates sole ulcers.
The digital cushion is designed to dissipate the cows weight (and keep the flexor tuberosity padded). However, the digital cushion gets thinner as the cow goes through each lactation. A low BCS (body condition score) has also been associated with a thinner digital cushion.
Per Cramer, the bovine foot is suspended by ligaments, rather than by laminae. So cows do not get laminitis but stretching of ligaments. Otherwise it sounds very similar! Most texts will refer to “laminitis”.
Deep digital flexor tendon and tendon sheath
As in the horse, the deep digital flexor tendon is surrounded by a tendon sheath as it passes caudal to the fetlock joint and inserts on the third phalanx. A navicular bursa helps it glide over the navicular bone.
This close proximity to the foot predisposes the tendon and tendon sheath to ascending infections. The coffin joint is similarly predisposed. Infections in the interdigital space (foot rot) and in the digit (abscesses) will often migrate upwards.
Vessels
To numb the foot for diagnostics or treatment, we often perform IV regional anesthesia
It is important to know the location of the veins so you can perform regional anesthesia (these are really hard to see on a live animal with a swollen limb). The best ones are dorsal and just in front of the dewclaws.
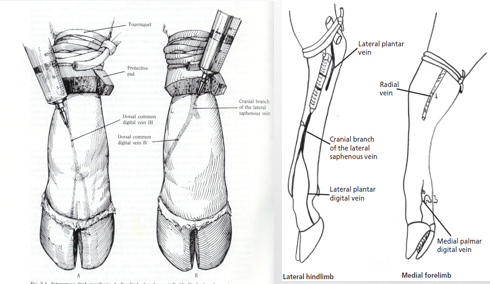
The vessel can also be stabbed by injecting perpendicular to the limb (parallel to the ground):
Review of digital anatomy, infectious causes of lameness and regional intravenous perfusion in cattle. KM Simpson et al. AABP 2020 (article will download)

