Bladder, Urethra and Ureters
How to – Perineal urethrostomy, ruminant
Indications
Perineal urethrostomy can be used for obstructive urolithiasis. PU is a short term fix in most ruminants due to rapid stricturing and reobstruction. It is considered a salvage procedure and is no longer commonly performed as penile amputation is easier.
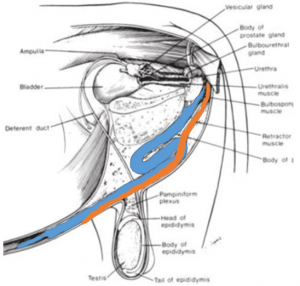
Relevant anatomy
The surgery needs to be performed proximal to the obstruction (typically the sigmoid flexure). The incision should stay on the vertical aspect of the perineum to avoid urine scald. The retractor penis muscles will be encountered first and are sometimes mistaken for the penis. They are paired, more superficial and less muscular than the penis.
Preoperative management
Food restrictions: NA. Surgery is performed standing and usually on an emergency basis.
NSAIDs/analgesics: Perioperative analgesics are necessary.
Antibiotics: Ascending infection is more likely postoperatively; however, the goal is salvage for slaughter.
Local blocks: Epidural anesthesia combined with local anesthesia if required.
Position/preparation: Standing
Surgery Supplies:
- Scalpel blade and handle
- Large hemostats (carmalts)
- Needle holders
- Thumb forceps
- Mayo scissors
- Suture scissors
- 2-0 and 0 absorbable suture, cutting needle
- Foley catheter, 20-28Fr with stylet (optional)
Surgical procedure
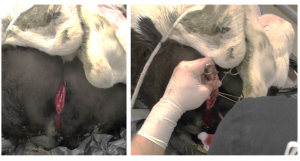
- Create a 10 cm vertical incision on midline, starting about 5 cm below the anus.
- Incise the dense fascia to expose the paired retractor penis muscles. These can be transected.
- Bluntly dissect between the muscles to the bulbospongiosus muscle with the palpable urethral groove immediately deep to the muscle
- Force a carmalt underneath the penis to stabilize it in the incision (optional).
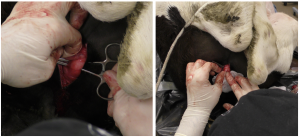
- Incise on midline to open the urethra. The urethra has a smooth mucosal surface and a catheter can be passed in either direction.
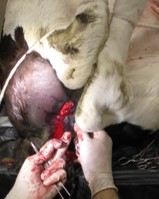
- The mucosa of the urethra is sutured to the skin using simple interrupted sutures, cruciates or short continuous runs.
- A catheter may be placed into the bladder to maintain urine flow for bladder or ruptured urethras.
Postoperative care
- Continue NSAIDs for 3 days
- Slaughter when uremia has resolved
Complications
- Urethral stricture and reobstruction
Videos
Perineal urethrostomy youtube video
Resources
Hooper and Taylor, Urinary Surgery. VCNA 1995, Vol.11(1), pp.95-121 – see page 111.

