1.8 Human Papillomavirus (HPV) and Cervical Cancer
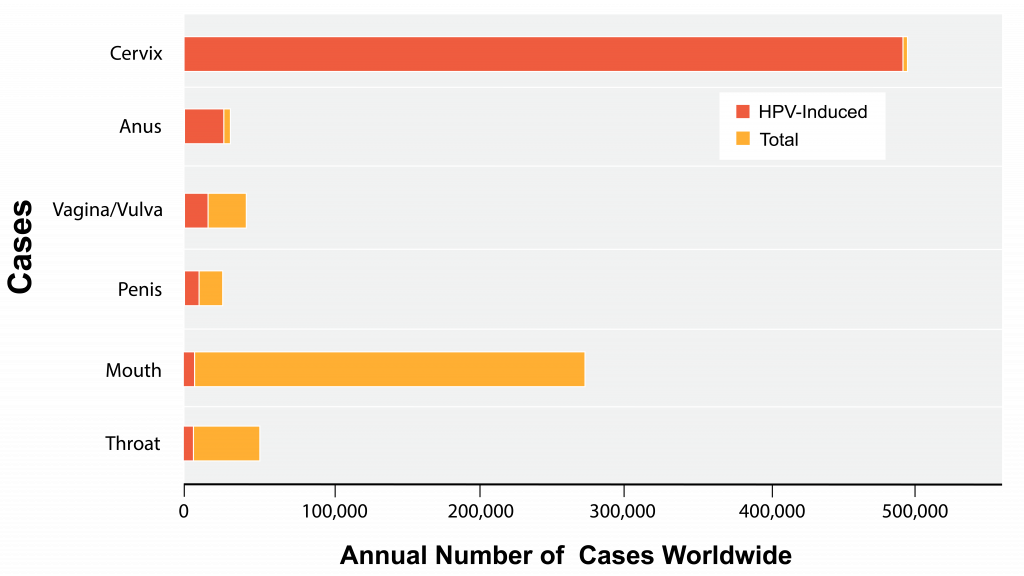
Following the observations of Brinton and others, scientists began to investigate a possible association between various infectious diseases and cervical cancer. Many years and studies later, we now know that HPV is associated with at least 90% of all documented cervical cancers. Smoking cigarettes also appears to place individuals at risk of developing cervical cancer. Some still suggest that using the Pill may be a contributing factor as well. However, there is compelling evidence implicating HPV as the cause of many types of cervical cancer. In fact, HPV is connected to other cancers as well–the following graph shows the annual number of cases of various cancers worldwide.
Points to Ponder
From the data below, what can you infer about the relationship between cervical cancer and HPV and the relationship between mouth cancer and HPV?
What is HPV?
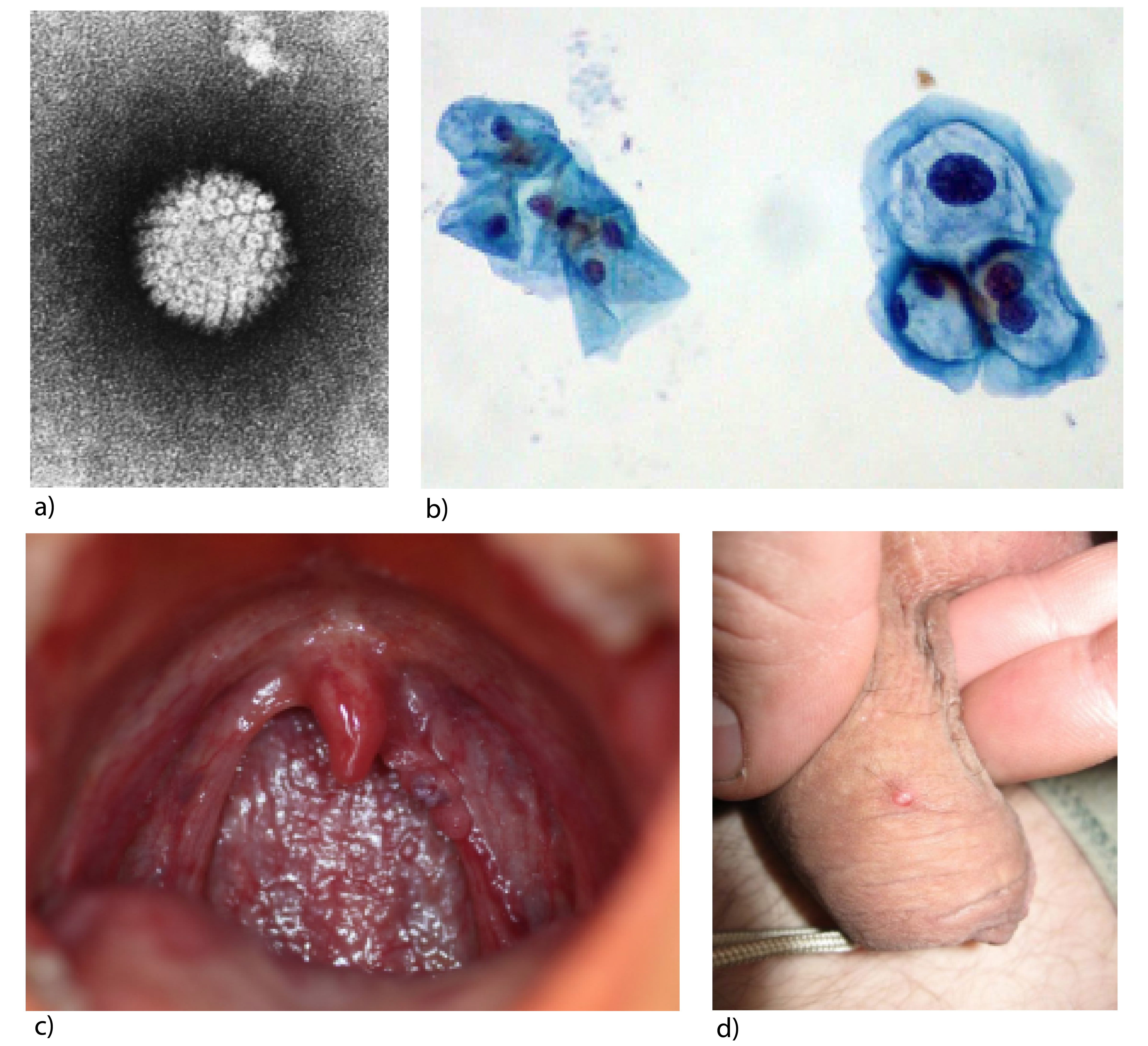
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a disease-causing virus and sexually transmitted disease, of the same name, that is typically diagnosed by the presence of genital warts. However, warts can occur in other places (e.g., the throat), and many individuals with HPV are undiagnosed. Therefore, it is important for women—whether they have been diagnosed with HPV or not—to have routine screenings (i.e., Pap smears) for cervical cancer. HPV prevention is challenging because there are many different strains of HPV. Consequently, the vaccines we currently use are designed to target several variations of the disease.