1.2 Nature of Science Overview
Science is a fact-based way of understanding natural phenomena. Science is really two things: (1) a collection of facts that have been established through observation or experimentation; and (2) a process for advancing knowledge about the natural world. We’ll discuss both established facts and science process in this text, but our emphasis will be on science as a process.
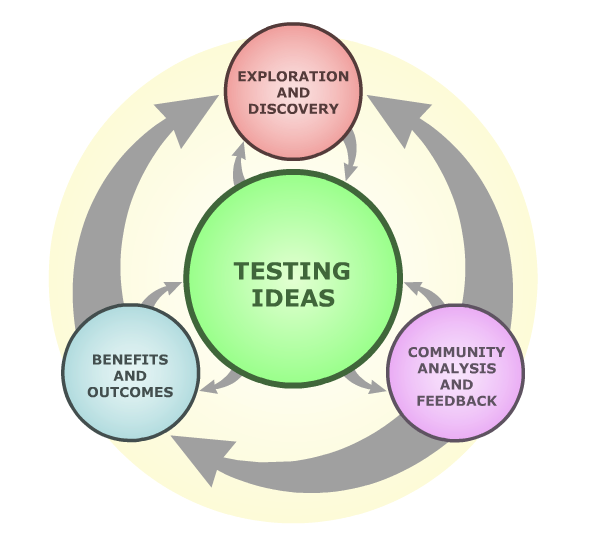
The process of science
Simply, the process of science includes making observations, generating questions and hypotheses about these observations, making and testing predictions, and revising the collective understanding through communication of our findings.
A hypothesis is a proposed explanation for some sort of natural phenomenon (such as male masturbation, female orgasm, or same-sex sexual preferences). By definition, a hypothesis sets the stage for further exploration, either through more observations or experimentation.
Check Yourself
Which of the following are testable hypotheses for the above questions?
a. Parents who disapprove of premarital sex are less likely to choose HPV vaccination for their offspring than do parents that are more accepting of premarital sex.
b. Homosexual behavior is genetic, in that homosexual individuals are more likely to have family members with same-sex sexual preferences.
c. The human female orgasm has the function of being associated with more successful copulations; specifically, women who orgasm are more likely to conceive during sex.
d. Young men masturbate frequently because frequent masturbation is a form of “sex practice” that makes men better sex partners.
- Copyright 2017 by The University of California Museum of Paleontology, Berkeley, and the Regents of the University of California. Used with permission. "How science works: The flowchart.." Understanding Science. University of California Museum of Paleontology. 3 January 2017 http://www.understandingscience.org/article/scienceflowchart. ↵

