1 Liver function
The liver receives nutrient rich blood directly from the gastrointestinal (GI) tract through the portal vein. The blood is modified by the liver before it moves onto other organs.
The liver is responsible for over 500 functions. The most crucial liver functions include:
Metabolism management
-
- we use nutrients from the gut and from liver stores to balance energy, build proteins, etc.
- all nutrient rich blood from the gut goes to the liver via the portal vein
- the liver either stores or releases compounds based on current metabolism needs
- catabolism – break down nutrients for storage
- anabolism – build up nutrients from stored components
Energy and nutrient storage
-
- the liver stores fats and carbohydrates in the form of triglycerides, lipoproteins and glycogen
- the liver stores B12 (cobalamin) and C vitamins, the fat soluble vitamins A, D,E and K, and iron and copper
Bile production and recirculation
-
- bile is necessary for fat digestion/absorption
- bile is important for emulsification of fats (turning large droplets into smaller droplets)
- bile is important for absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A,D, E and K)
- bile is a combination of components including bile acids (made from cholesterol) and bilirubin pigment (from degraded red blood cells)
- the enterohepatic recirculation system returns most of the bile to the liver for re-use
-
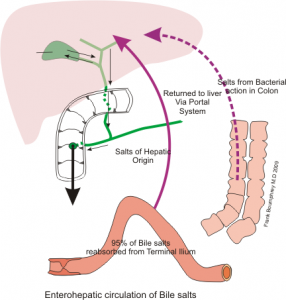
https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/f/f4/Bile_recycling.png
- bile is necessary for fat digestion/absorption
Protein formation
-
- the liver creates proteins required for coagulation, binding of and building of other proteins, transport of iron and other compounds, immune function, and vascular pressure (oncotic pressure)
- the liver creates cholesterol which means cholesterol can be measured as an indicator of liver function
Detoxification
-
- the liver denatures toxins, potential toxins (drugs), ammonia (urea cycle) and old red blood cells
Drug metabolism
-
- the liver may activate or inactivate drugs, depending upon the drug, drug combination and specific enzymes
- cytochrome p450 enzymes are essential
Resources
What is bile – video
Liver function Khan academy – includes P450 enzymes, bioavailability and more
Secretion of bile and the role of bile acids in digestion -short, sweet and useful
Hepatic lobule – review of the microscopic anatomy – portal triad; Khan Academy
The liver- functions – Neural academy video
Bile acid formation and function – Osmosis video
Just for fun

