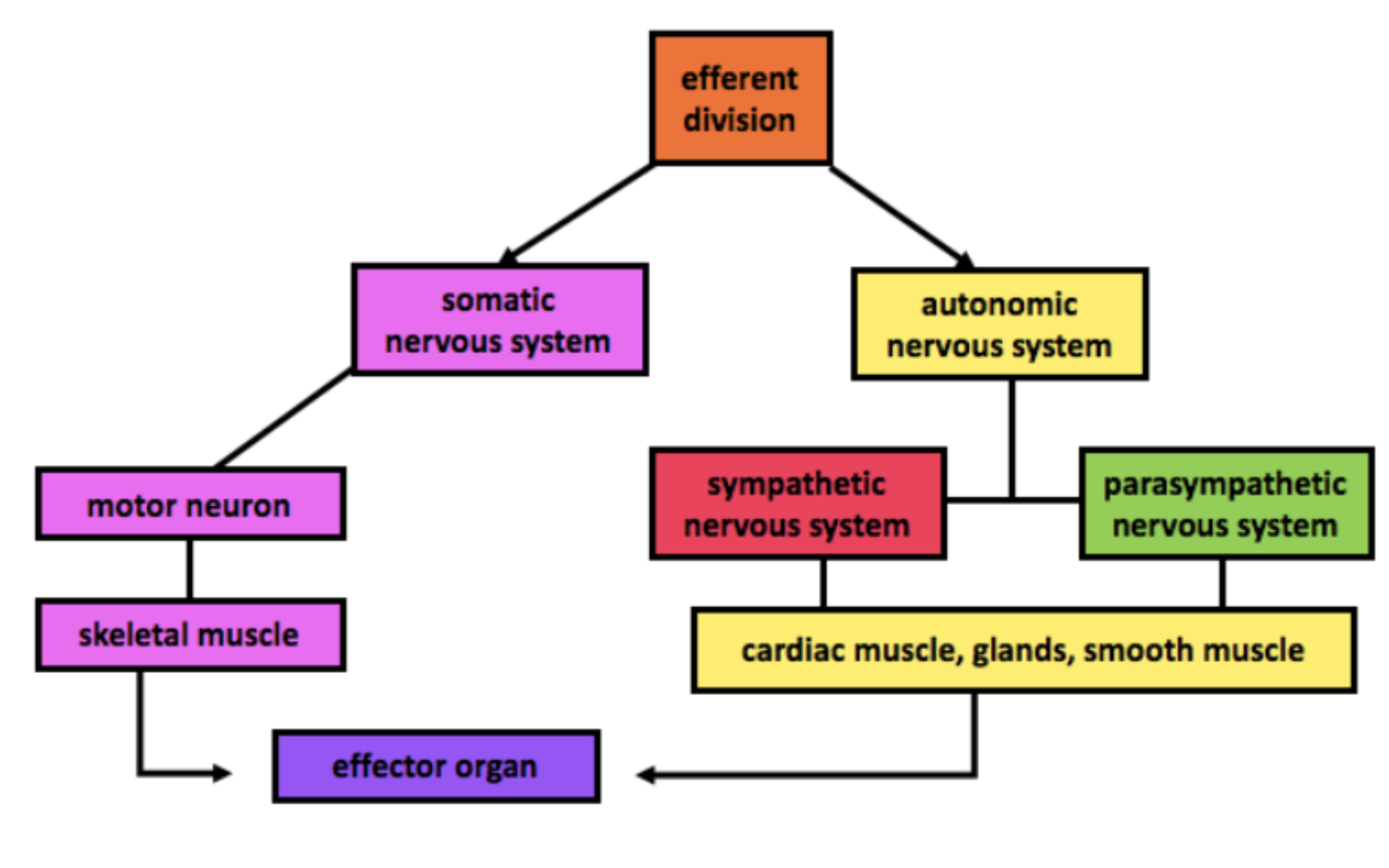
Main Body
21. Agents and Actions of the Autonomic Nervous System: Parasympathetic Nervous System
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Parasympathetic Nervous System [PNS] – “rest and digest”
The PNS can also be thought of as the “D” division – defecation, digestion, and diuresis
Most organs are innervated with parasympathetic nerve ganglions.
EXCEPTION – the ciliary smooth muscle of the eye only has parasympathetic innervation
What does your body need when at rest?
- Decreased cardiac output (compared to sympathetic) – lower oxygen demand when at rest
- Energy storage (glycogenesis, lipogenesis) – lower energy demand at rest
- Increased digestion – increased GI motility and secretions
- Waste elimination – defecation and urination
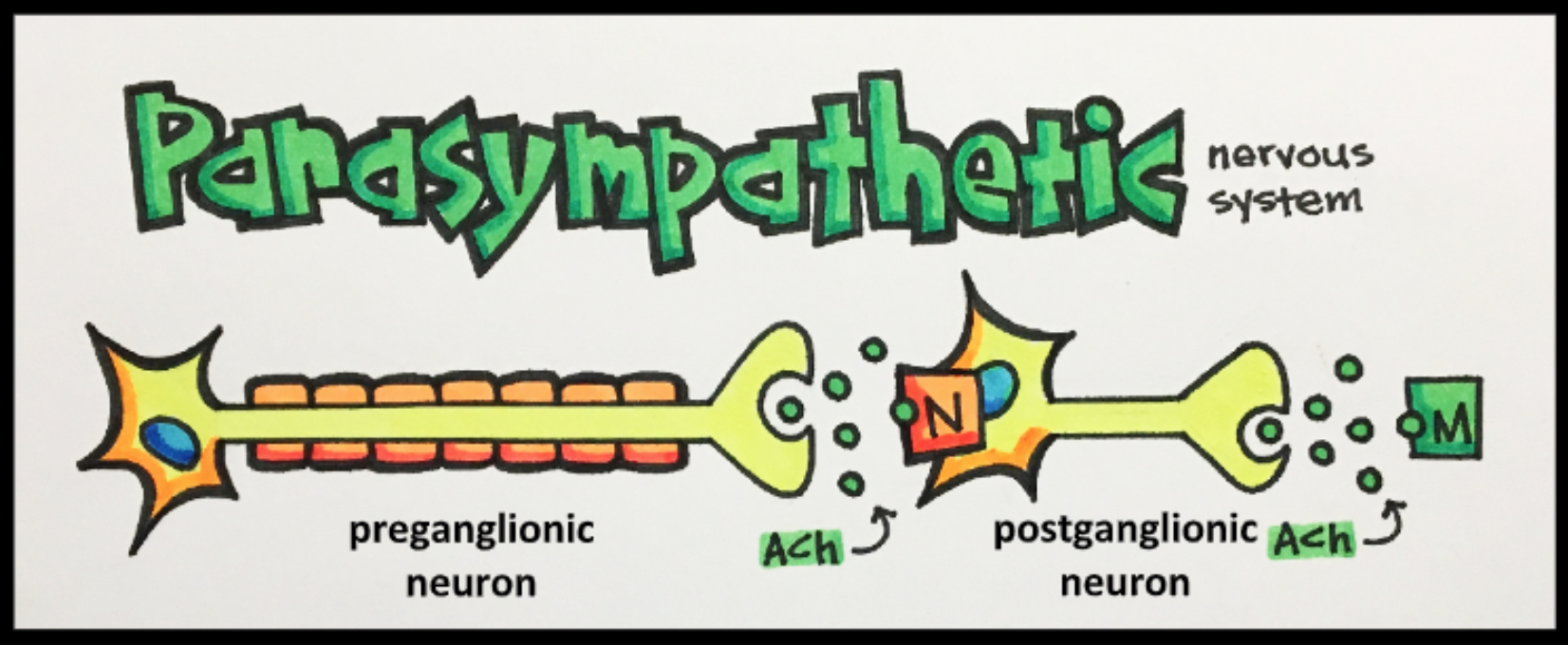
Parasympathetic Neurons
Pre-ganglionic and post-ganglionic parasympathetic neurons release acetylcholine [ACh].
Acetylcholine
Acetylcholine interacts with two types of receptors:
- Nicotinic receptors – located on ganglion
- Muscarinic receptors – located on effector organ/tissue
- M1 –
- M2 –
- M3 –
- M4 –
- M5 –
Physiological Effects of PNS on Organs/Tissue & Respective Receptors
| Organ/Tissue | Receptor Subtype | Physiological Effect | |
|---|---|---|---|
| BLADDER – detrusor | M3 | contracts | promotes urination |
| BLADDER – sphincter | M3 | relaxes | promotes urination |
| EYE – ciliary muscle | M3 | contracts | improves near-sighted vision |
| EYE – pupil | M3 | contracts | |
| GASTROINTESTINAL – glands | M3 | promotes secretion | enhances digestion |
| GASTROINTESTINAL – smooth muscle | M3 | contracts | enhances digestion & motility |
| GASTROINTESTINAL – sphincter | M3 | relaxes | promotes defecation |
| HEART – AV node | M2 | decreases conduction | |
| HEART – cardiac muscle | M2 | decreases contractility | negative ionotropic effect [atria only] |
| HEART – cardiac output | M2 | decreases | decreases blood delivery |
| HEART – SV node | M2 | decreased heart rate | negative chronotropic effect – decreases oxygen delivery |
| LUNG – smooth muscle (bronchioles & trachea) | M3 | contracts | |
| SALIVARY GLAND | M3 | stimulates watery secretions | enhances digestion |
| VASCULATURE – smooth muscle | no PNS innervation |