Main Body
2. Introduction to Drug-Receptor Interactions and Pharmacodynamics
Receptors: protein molecules including enzymes, transporters and ion channels where a ligand (specific endogenous neurotransmitter/hormone or an external pharmacological agent (drug)) binds to, resulting in a cellular response.
- Unique Exception: Orphan Receptors are receptors for which the ligand remains unknown.
- Reminder: Ligand is an ion or molecule that forms a complex with a biomolecule to serve a specific biological purpose
Examples of Endogenous Ligands:
-
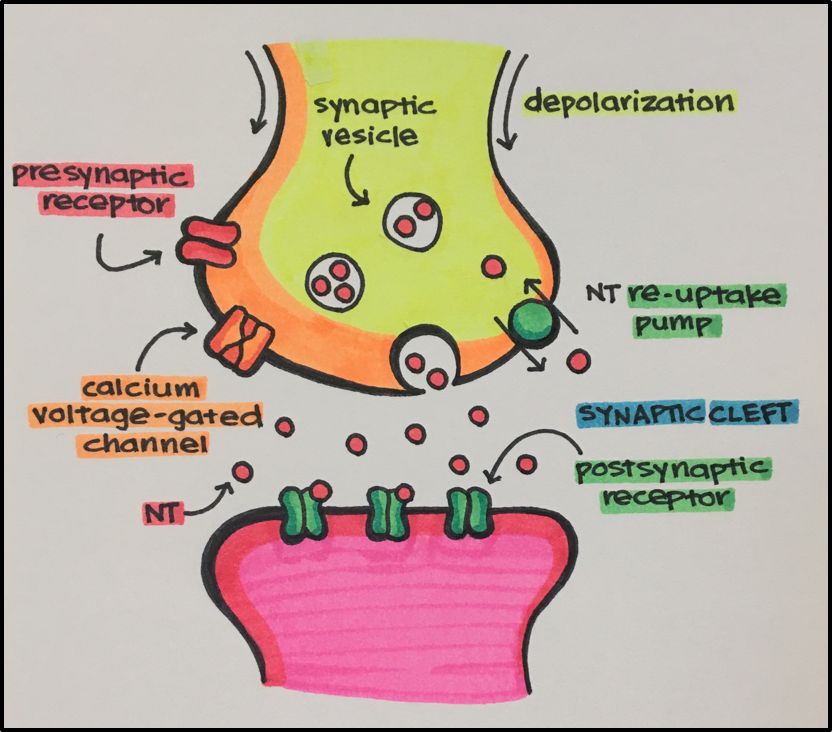
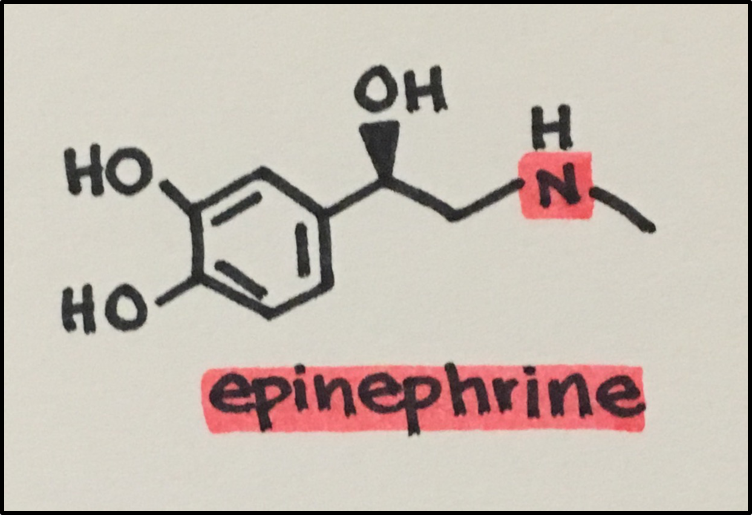
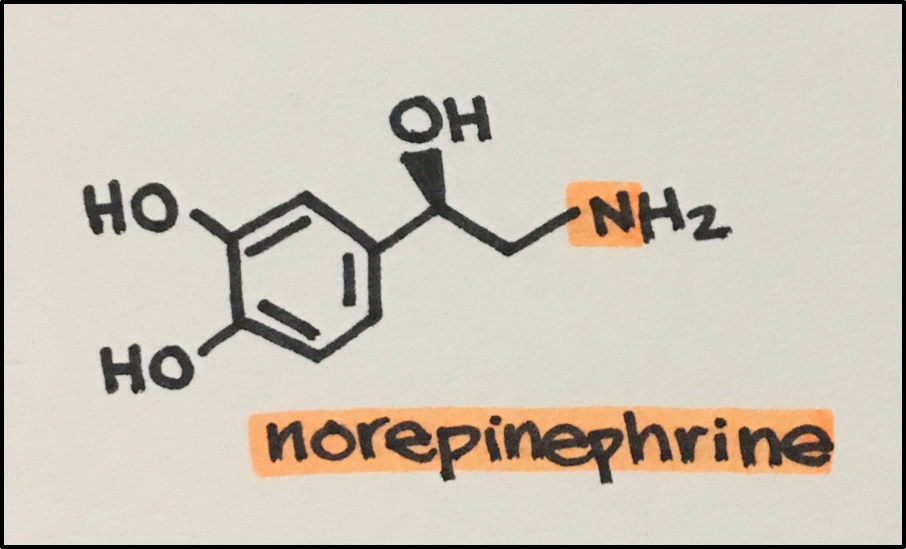
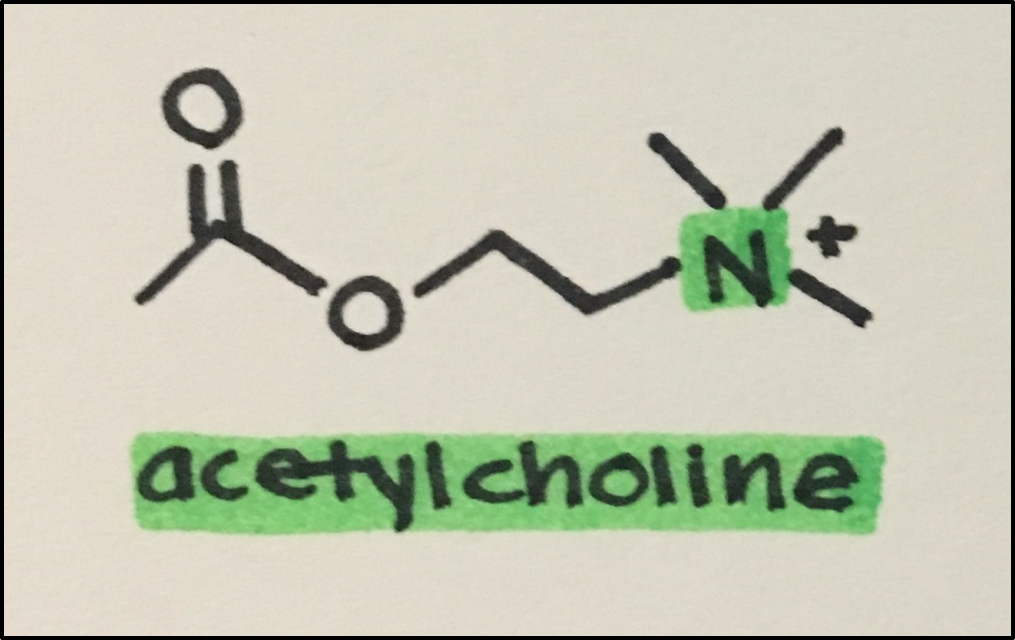
- Neurotransmitters[NT]: chemical messengers signaling across a synaptic cleft
- Acetylcholine [Ach]
- Epinephrine [EPI]
- Norepinephrine [NE]
- Neurotransmitters[NT]: chemical messengers signaling across a synaptic cleft
 |
 |
 |
-
- Hormones (peptide): secreted from neuroendocrine cells into the blood to signal at distant cells and tissues.
- Aldosterone
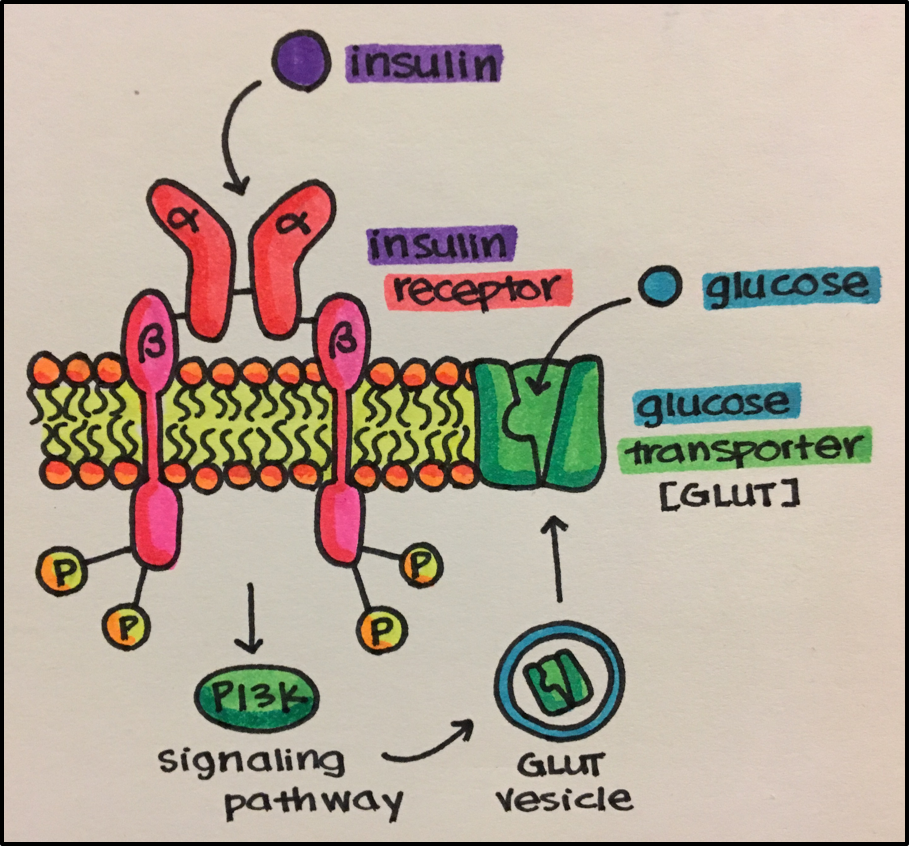
- Insulin
- Nerve growth factor [NGF]
- Thyroid hormone [TH]
- Hormones (peptide): secreted from neuroendocrine cells into the blood to signal at distant cells and tissues.
- Insulin is synthesized and released by pancreatic beta cells. It is transported through the blood to a variety of cells to stimulate those cells to express glucose transporters allowing those cells to bring glucose into the cell for energy utilization.
DRUG: A chemical agent that selectively interacts with specific target molecules (i.e. receptors) to alter their specific physiological functions.
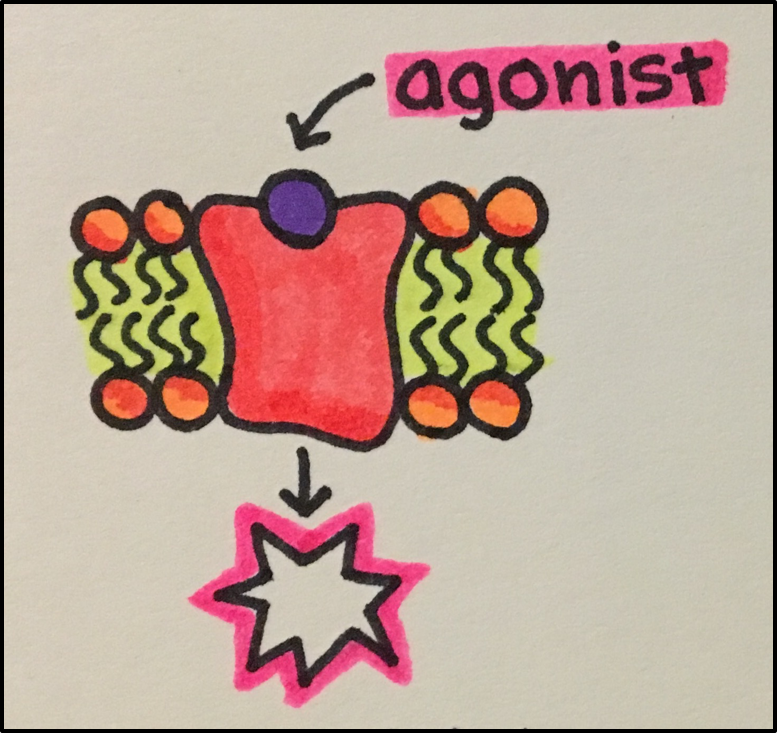
- Agonist: drug that activates receptors to result in either stimulation or inhibition of the function of various types of cells and organs.
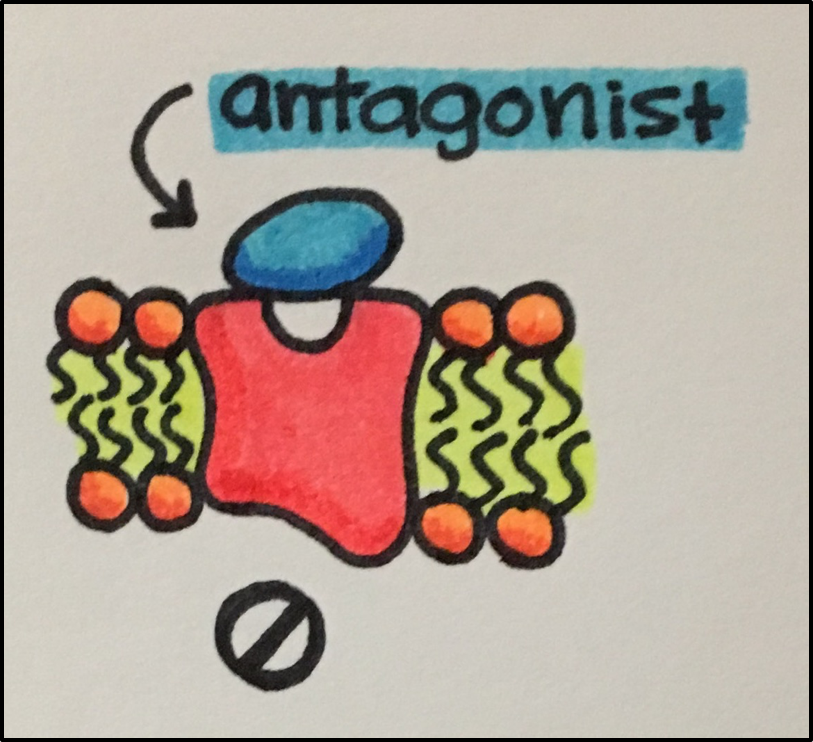
- Antagonist: drug that prevents receptor activation by agonists.
Drug-Receptor Binding: drugs bind to their respective receptor in a variety of ways depending on their characteristics.
- Ionic interaction: cation & anion
- Hydrogen bonding
- Lipophilic interaction
- Covalent bond: irreversible