Main Body
5. Drug Action vs. Drug Effect
Drug Action: drug-receptor interaction that results in a change in the tertiary structure of the receptor (conformational change) by agonists
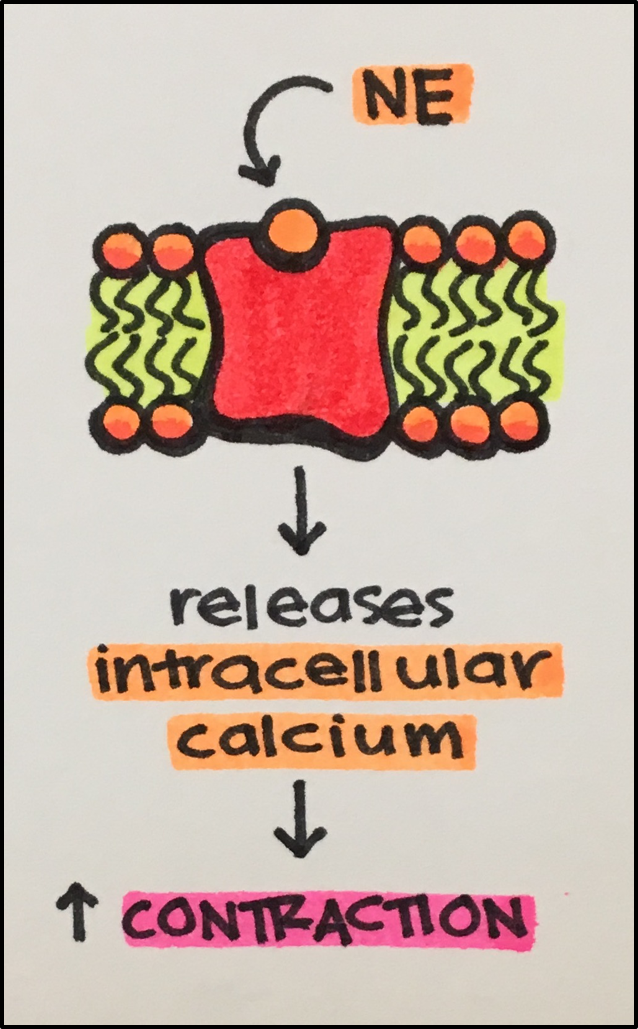
- See right: Norepinephrine [NE] acts as an agonist, activating its receptor to initiate a cascade of cellular events.
Drug/Pharmacological Effect: specific changes in physiological function as a result of drug interaction with a particular receptor.
- See right: the drug-receptor interaction leads to a cascade of events ultimately causing the heart to contract.