1. Human Reproductive Anatomy
Human Reproductive Anatomy
In general, the reproductive structures in humans can be divided into three main categories: gonads, internal genitalia and external genitalia. The gonads are the organs in which gametes, the cells that fuse in fertilization to form new individuals, develop and mature. All other reproductive structures are called genitalia, or genitals. Internal genitalia are found inside of the body, while external genitalia are visible from the outside. The structures seen in adult males and females actually come from the same precursors in embryos, so there are many similarities in both structure and function between males and females. There is also a wide spectrum of structures present in any one individual; many people have structures that resemble a combination of male and female structures, or that resemble neither. In this textbook, we will define “male” and “female” based on individuals who have the most typical structures characteristic of those two sexes; other types of structures are also normal and common. We will describe the functions of these structures during vaginal sexual intercourse, since that is the sexual act used in reproduction; keep in mind that other types of sexual activity are also common and normal.
Male Reproductive Anatomy
In the male reproductive system, the scrotum houses the testicles or testes (singular: testis), including providing passage for blood vessels, nerves, and muscles related to testicular function. The testes are gonads, and they produce sperm (the male gametes) and some reproductive hormones. Each testis is approximately 2.5 by 3.8 cm (1.5 by 1 in) in size and divided into wedge-shaped lobules by connective tissue called septa.
Sperm are immobile at body temperature; therefore, the scrotum and penis are external to the body, as illustrated in Figure 1 so that a proper temperature is maintained for motility.
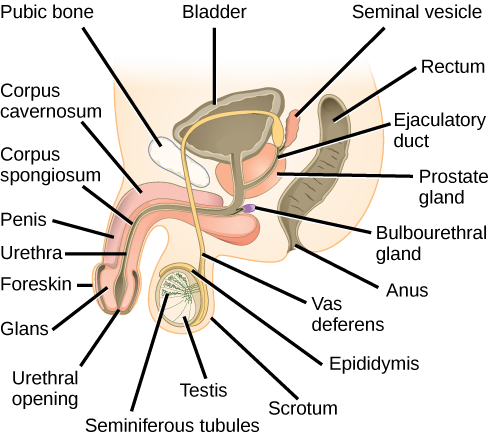
The internal genitalia in males are important for the production of sperm, and of other components of . the semen. Sperm mature in seminiferous tubules that are coiled inside the testes, as illustrated in Figure 1. The walls of the seminiferous tubules are made up of the developing sperm cells, with the least developed sperm at the periphery of the tubule and the fully developed sperm in the lumen. The sperm cells are mixed with “nursemaid” cells called Sertoli cells which protect the germ cells and promote their development. Other cells mixed in the wall of the tubules are the interstitial cells of Leydig. These cells produce high levels of testosterone once the male reaches adolescence.
When the sperm have developed flagella and are nearly mature, they leave the testicles and enter the epididymis, shown in Figure 1. This structure resembles a comma and lies along the top and posterior portion of the testes; it is the site of sperm maturation. The sperm leave the epididymis and enter the vas deferens (or ductus deferens), which carries the sperm, behind the bladder, and forms the ejaculatory duct with the duct from the seminal vesicles. During a vasectomy, a section of the vas deferens is removed, preventing sperm from being passed out of the body during ejaculation and preventing fertilization.
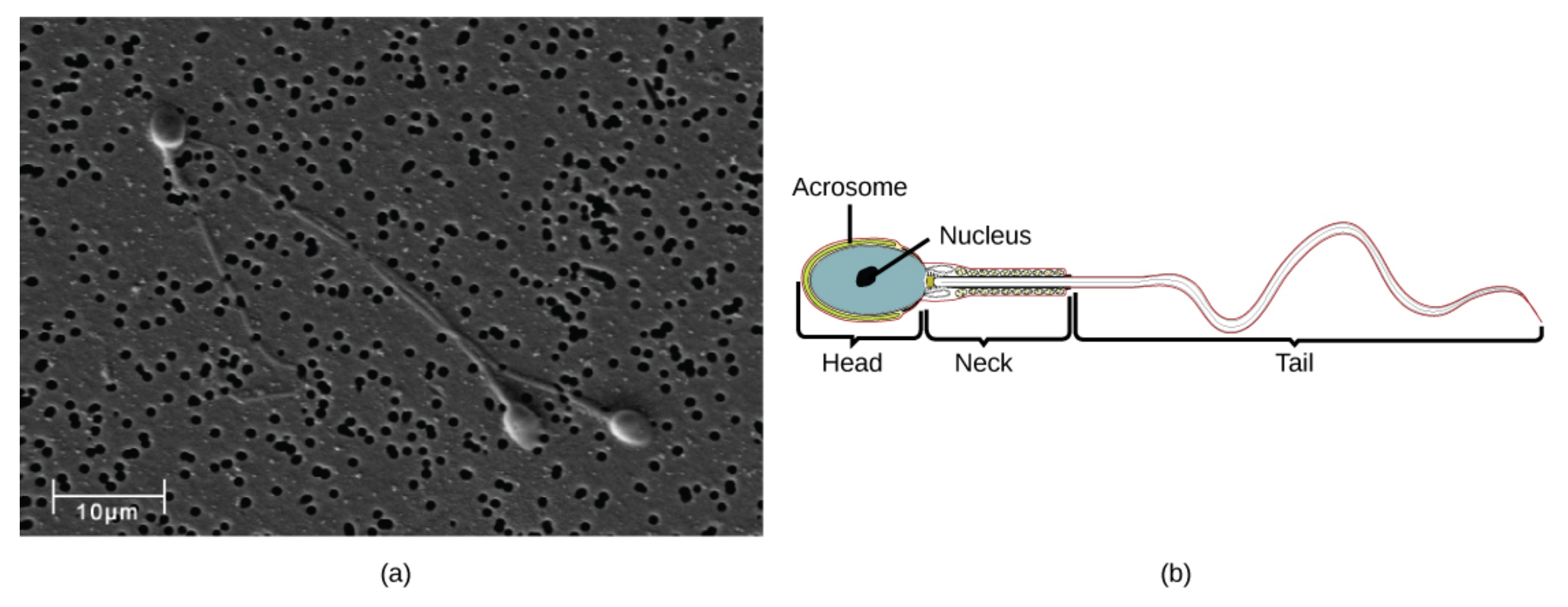
Semen is a mixture of sperm and spermatic duct secretions (about 10 percent of the total) and fluids from accessory glands that contribute most of the semen’s volume. Sperm are haploid cells, consisting of a flagellum as a tail, a neck that contains the cell’s energy-producing mitochondria, and a head that contains the genetic material. Figure 2 shows a micrograph of human sperm as well as a diagram of the parts of the sperm. An acrosome is found at the top of the head of the sperm. This structure contains enzymes that can digest the protective coverings that surround the egg to help the sperm penetrate and fertilize the egg. An ejaculate (a single emission of sperm) will contain from two to five milliliters of fluid with from 50–120 million sperm per milliliter.
The bulk of the semen comes from the accessory glands associated with the male reproductive system. These are the seminal vesicles, the prostate gland, and the bulbourethral gland, all of which are illustrated in Figure 1. The seminal vesicles are a pair of glands that lie along the posterior border of the urinary bladder. The glands make a solution that is thick, yellowish, and alkaline. As sperm are only motile in an alkaline environment, a basic pH is important to reverse the acidity of the vaginal environment. The solution also contains mucus, fructose (a sperm mitochondrial nutrient), a coagulating enzyme, ascorbic acid, and local-acting hormones called prostaglandins. The seminal vesicle glands account for 60 percent of the bulk of semen.
The penis, illustrated in Figure 1, is an organ that drains urine from the renal bladder and functions as a copulatory organ during intercourse. The penis contains three tubes of erectile tissue running through the length of the organ. These consist of a pair of tubes on the dorsal side, called the corpus cavernosum, and a single tube of tissue on the ventral side, called the corpus spongiosum. This tissue will become engorged with blood, becoming erect and hard, in preparation for sexual intercourse. The organ is inserted into the vagina culminating with an ejaculation. During intercourse, the smooth muscle sphincters at the opening to the renal bladder close and prevent urine from entering the penis. An orgasm is a two-stage process: first, glands and accessory organs connected to the testes contract, then semen (containing sperm) is expelled through the urethra during ejaculation. After intercourse, the blood drains from the erectile tissue and the penis becomes flaccid.
The walnut-shaped prostate gland surrounds the urethra, the connection to the urinary bladder. It has a series of short ducts that directly connect to the urethra. The gland is a mixture of smooth muscle and glandular tissue. The muscle provides much of the force needed for ejaculation to occur. The glandular tissue makes a thin, milky fluid that contains citrate (a nutrient), enzymes, and prostate specific antigen (PSA). PSA is a proteolytic enzyme that helps to liquefy the ejaculate several minutes after release from the male. Prostate gland secretions account for about 30 percent of the bulk of semen.
The bulbourethral gland, or Cowper’s gland, releases its secretion prior to the release of the bulk of the semen. It neutralizes any acid residue in the urethra left over from urine. This usually accounts for a couple of drops of fluid in the total ejaculate and may contain a few sperm. Withdrawal of the penis from the vagina before ejaculation to prevent pregnancy may not work if sperm are present in the bulbourethral gland secretions. The location and functions of the male reproductive organs are summarized in Table 1.
| Organ | Location | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Scrotum | External | Carry and support testes |
| Penis | External | Deliver urine, copulating organ |
| Seminiferous Tubules | Internal | Site of sperm maturation in testes |
| Epididymus | Internal | Part of pathway for sperm exit from body |
| Vas Deferens | Internal | Part of pathway for sperm exit from body |
| Ejaculatory Duct | Internal | Site of mixing of sperm with semen components, part of pathway for sperm exit from body |
| Testes | Internal | Produce sperm and male hormones |
| Seminal Vesicles | Internal | Contribute to semen production |
| Prostate Gland | Internal | Contribute to semen production |
| Bulbourethral Glands | Internal | Clean urethra at ejaculation |
Female Reproductive Anatomy
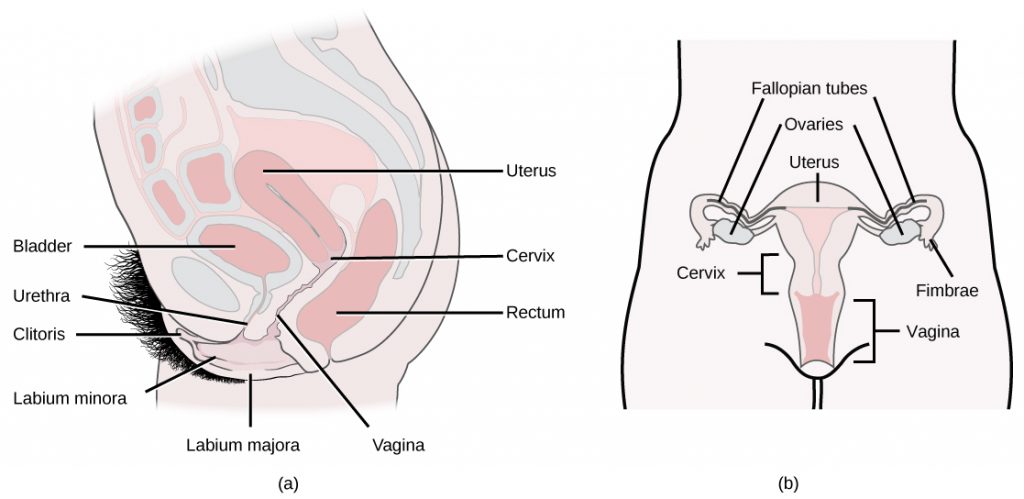
A number of reproductive structures are exterior to the female’s body. These include the breasts and the vulva, which consists of the mons pubis, clitoris, labia majora, labia minora, and the vestibular glands, all illustrated in Figure 3. The location and functions of the female reproductive organs are summarized in Table 2. The mons pubis is a round, fatty area that overlies the pubic bone. The clitoris is a structure with erectile tissue that contains a large number of sensory nerves and serves as a source of stimulation during intercourse. The labia majora are a pair of elongated folds of tissue that run posterior from the mons pubis and enclose the other components of the vulva. The labia majora derive from the same tissue that produces the scrotum in a male. The labia minora are thin folds of tissue centrally located within the labia majora. These labia protect the openings to the vagina and urethra. The mons pubis and the anterior portion of the labia majora become covered with hair during adolescence; the labia minora is hairless. The greater vestibular glands are found at the sides of the vaginal opening and provide lubrication during intercourse.The vulva is the name for the entire set of external genitalia in the inguinal (groin) area of females; in common language this is sometimes referred to as the vagina, but that is not anatomically accurate; the vagina is an entirely internal structure.
| Organ | Location | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Clitoris | External | Sensory organ |
| Mons pubis | External | Fatty area overlying pubic bone |
| Labia majora | External | Covers labia minora |
| Labia minora | External | Covers vestibule |
| Greater vestibular glands | External | Secrete mucus; lubricate vagina |
| Breast | External | Produce and deliver milk |
| Ovaries | Internal | Carry and develop eggs |
| Oviducts (Fallopian tubes) | Internal | Transport egg to uterus |
| Uterus | Internal | Support developing embryo |
| Vagina | Internal | Common tube for intercourse, birth canal, passing menstrual flow |
The breasts consist of mammary glands and fat. The size of the breast is determined by the amount of fat deposited behind the gland. Each gland consists of 15 to 25 lobes that have ducts that empty at the nipple and that supply the nursing child with nutrient- and antibody-rich milk to aid development and protect the child.
Internal female reproductive structures include ovaries, oviducts, the uterus, and the vagina, shown in Figure 3. The two ovaries (the female gonads) are held in place in the abdominal cavity by a system of ligaments. Ovaries consist of a medulla and cortex: the medulla contains nerves and blood vessels to supply the cortex with nutrients and remove waste. The outer layers of cells of the cortex are the functional parts of the ovaries. The cortex is made up of follicular cells that surround eggs that develop during fetal development in utero. During the menstrual period, a batch of follicular cells develops and prepares the eggs for release. At ovulation, one follicle ruptures and one egg is released, as illustrated in Figure 4a.
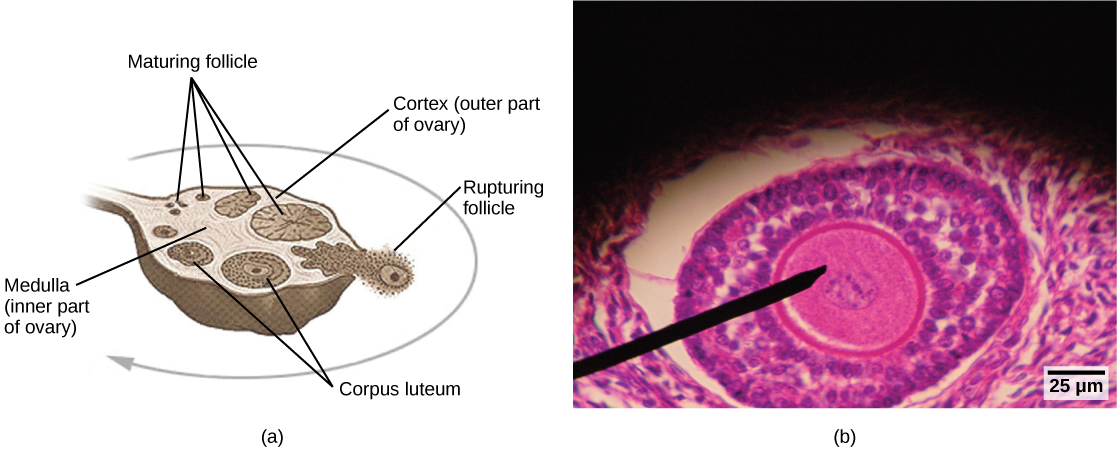
The oviducts, or fallopian tubes, extend from the uterus in the lower abdominal cavity to the ovaries, but they are not in contact with the ovaries. The lateral ends of the oviducts flare out into a trumpet-like structure and have a fringe of finger-like projections called fimbriae, illustrated in Figure 4b. When an egg is released at ovulation, the fimbrae help the non-motile egg enter into the tube and passage to the uterus. The walls of the oviducts are ciliated and are made up mostly of smooth muscle. The cilia beat toward the middle, and the smooth muscle contracts in the same direction, moving the egg toward the uterus. Fertilization usually takes place within the oviducts and the developing embryo is moved toward the uterus for development. It usually takes the egg or embryo a week to travel through the oviduct. Sterilization in females is called a tubal ligation; it is analogous to a vasectomy in males in that the oviducts are severed and sealed.
The uterus is a structure about the size of a females’s fist. This is lined with an endometrium rich in blood vessels and mucus glands. The uterus supports the developing embryo and fetus during gestation. The thickest portion of the wall of the uterus is made of smooth muscle. Contractions of the smooth muscle in the uterus aid in passing the baby through the vagina during labor. A portion of the lining of the uterus sloughs off during each menstrual period, and then builds up again in preparation for an implantation. Part of the uterus, called the cervix, protrudes into the top of the vagina. A small opening called the cervical orifice allows menstrual fluid out of the cervix into the vagina, and sperm into the uterus. During childbirth the cervical orifice is greatly enlarged.
The vagina is a muscular tube that serves several purposes. It allows menstrual flow to leave the body. It is the receptacle for the penis during intercourse and the vessel for the delivery of offspring. It is lined cells that produce acidic secretions that limit the growth of microbes that could potentially travel into the uterus.
Development of Reproductive Organs in Humans.
The reproductive tissues of male and female humans develop similarly in utero (in a fetus developing in the mother’s uterus) for the first several weeks of gestation. The hormone testosterone is typically only released in embryos that have a male sex chromosome (the Y chromosome, discussed in the next chapter), and this hormone controls the generation of reproductive structures. A low level of the hormone testosterone is released from male gonads in the developing embryos, starting at around the second month of gestation. Testosterone causes the undeveloped tissues to differentiate into male sexual organs. When testosterone is absent, the tissues develop into female sexual tissues. Primitive gonads become testes or ovaries. Tissues that produce a penis in males produce a clitoris in females. The tissue that will become the scrotum in a male becomes the labia in a female; that is, they are homologous structures. Because of this, there are often variations in development resulting in structures that may have characteristics of both sexes, or of neither sex, depending on hormonal levels and other factors present during embryogenesis. These variations in sexual structures are quite common and normal.
Sexual Response During Intercourse
The sexual response in humans is both psychological and physiological. Both sexes experience sexual arousal through psychological and physical stimulation. There are four phases of the sexual response. During phase one, called excitement, vasodilation leads to vasocongestion in erectile tissues in both males and females. The nipples, clitoris, labia, and penis engorge with blood and become enlarged. Vaginal secretions are released to lubricate the vagina to facilitate intercourse. During the second phase, called the plateau, stimulation continues, the outer third of the vaginal wall enlarges with blood, and breathing and heart rate increase.
During phase three, or orgasm, rhythmic, involuntary contractions of muscles occur in both sexes. In the male, the reproductive accessory glands and tubules constrict placing semen in the urethra, then the urethra contracts expelling the semen through the penis. In females, the uterus and vaginal muscles contract in waves that may last slightly less than a second each. During phase four, or resolution, the processes described in the first three phases reverse themselves and return to their normal state. Males experience a refractory period in which they cannot maintain an erection or ejaculate for a period of time ranging from minutes to hours.
Section Summary
The reproductive structures that evolved in humans allow males and females to mate, fertilize internally, and support the growth and development of offspring. Reproductive structures include gonads, internal and external genitalia. Some male and female reproductive structures have analogous functions and are derived from common precursor structures. Both males and females have four stages of the sexual response.
Glossary
- bulbourethral gland
- secretion that cleanses the urethra prior to ejaculation
- clitoris
- sensory structure in females; stimulated during sexual arousal
- external genitalia
- reproductive structures visible on the outside of the body
- gametes
- haploid cells that combine in fertilization to produce a new diploid individual; eggs and sperm
- gametogenesis
- the process of egg or sperm development
- gonads
- structures that produce gametes (eggs and sperm);female gonads are ovaries and male gonads are testes
- internal genitalia
- all internal reproductive structures except for gonads
- interstitial cells of Leydig
- cells in the testes that produce testosterone, also called Leydig cells
- labia majora
- large folds of tissue covering the inguinal area
- labia minora
- smaller folds of tissue within the labia majora
- oviduct
- (also, fallopian tube) muscular tube connecting the uterus with the ovary area
- penis
- male reproductive structure for urine elimination and copulation
- prostate gland
- structure that is a mixture of smooth muscle and glandular material and that contributes to semen
- scrotum
- sac containing testes; exterior to the body
- semen
- fluid mixture of sperm and supporting materials
- seminal vesicle
- secretory accessory gland in males; contributes to semen
- seminiferous tubule
- site of sperm production in testes
- Sertoli cells
- cells inside of the testes that protect sperm and help them to mature
- testes
- pair of reproductive organs in males
- uterus
- environment for developing embryo and fetus
- vagina
- muscular tube for the passage of menstrual flow, copulation, and birth of offspring
-
CC LICENSED CONTENT, SHARED PREVIOUSLY
OpenStax, Concepts of Biology, Section 18.3 Human Reproduction
Provided by: Rice University
Access for free at https://openstax.org/details/books/concepts-biology
License: CC-BY 4.0
Adapted By: Sarah Malmquist

