7. ATP: Adenosine Triphosphate
Almost all chemical reactions in human cells require energy. Within the cell, from where does energy to power such reactions come? The answer lies with an energy-supplying molecule scientists call adenosine triphosphate, or ATP. This is a small, relatively simple molecule (Figure 1), but within some of its bonds, it contains the potential for a quick burst of energy that can be harnessed to perform cellular work. Think of this molecule as the cells’ primary energy currency in much the same way that money is the currency that people exchange for things they need. ATP powers the majority of energy-requiring cellular reactions.
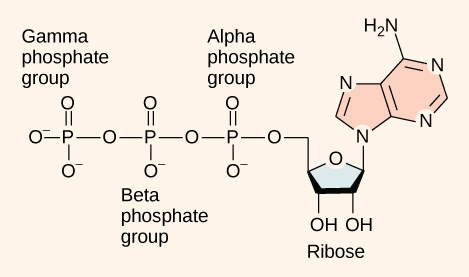
As its name suggests, adenosine triphosphate is comprised of adenosine bound to three phosphate groups (Figure 1). Adenosine is a nucleoside consisting of the nitrogenous base adenine and a five-carbon sugar, ribose. The three phosphate groups, in order of closest to furthest from the ribose sugar, are alpha, beta, and gamma. Together, these chemical groups constitute an energy powerhouse. However, not all bonds within this molecule exist in a particularly high-energy state. Both bonds that link the phosphates are equally high-energy bonds (phosphoanhydride bonds) that, when broken, release sufficient energy to power a variety of cellular reactions and processes. These high-energy bonds are the bonds between the second and third (or beta and gamma) phosphate groups and between the first and second phosphate groups. These bonds are “high-energy” because the products of such bond breaking—adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and one inorganic phosphate group (Pi)—have considerably lower free energy than the reactants: ATP and a water molecule. Because this reaction takes place using a water molecule, it is a hydrolysis reaction. In other words, ATP hydrolyzes into ADP in the following reaction:
ATP + H2O → ADP + Pi + free energy
Like most chemical reactions, ATP to ADP hydrolysis is reversible. The reverse reaction regenerates ATP from ADP + Pi. Cells rely on ATP regeneration just as people rely on regenerating spent money through some sort of income. Since ATP hydrolysis releases energy, ATP regeneration must require an input of free energy. This equation expresses ATP formation:
ADP + Pi + free energy → ATP + H2O
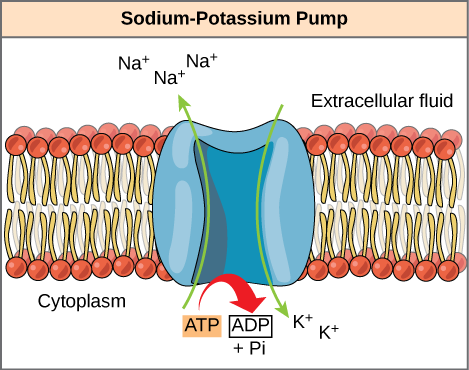
ATP is a highly unstable molecule. Unless quickly used to perform work, ATP spontaneously dissociates into ADP + Pi, and the free energy released during this process is lost as heat. Cells can harness the energy released during ATP hydrolysis by using energy coupling, where the process of ATP hydrolysis is linked to other processes in the cell. One example of energy coupling using ATP involves a transmembrane ion pump that is extremely important for cellular function. This sodium-potassium pump (Na+/K+ pump) drives sodium out of the cell and potassium into the cell (Figure 2). A large percentage of a cell’s ATP powers this pump, because cellular processes bring considerable sodium into the cell and potassium out of it. The pump works constantly to stabilize cellular concentrations of sodium and potassium. In order for the pump to turn one cycle (exporting three Na+ ions and importing two K+ ions), one ATP molecule must hydrolyze. When ATP hydrolyzes, its gamma phosphate does not simply float away, but it actually transfers onto the pump protein. Scientists call this process of a phosphate group binding to a molecule phosphorylation. As with most ATP hydrolysis cases, a phosphate from ATP transfers onto another molecule. In a phosphorylated state, the Na+/K+ pump has more free energy and is triggered to undergo a conformational change (a change in the shape of the protein.) This change allows it to release Na+to the cell’s outside. It then binds extracellular K+, which, through another conformational change, causes the phosphate to detach from the pump. This phosphate release triggers the K+ to release to the cell’s inside. Essentially, the energy released from the ATP hydrolysis couples with the energy required to power the pump and transport Na+ and K+ ions. ATP performs cellular work using this basic form of energy coupling through phosphorylation.
Often during cellular metabolic reactions, such as nutrient synthesis and breakdown, certain molecules must alter slightly in their conformation to become substrates for the next step in the reaction series. One example is during the very first steps of cellular respiration, when a sugar glucose molecule breaks down in the process of glycolysis. In the first step, ATP is required to phosphorylze glucose, creating a high-energy but unstable intermediate. This phosphorylation reaction powers a conformational change that allows the phosphorylated glucose molecule to convert to the phosphorylated sugar fructose. Fructose is a necessary intermediate for glycolysis to move forward. Here, ATP hydrolysis’ exergonic reaction couples with the endergonic reaction of converting glucose into a phosphorylated intermediate in the pathway. Once again, the energy released by breaking a phosphate bond within ATP was used for phosphorylyzing another molecule, creating an unstable intermediate and powering an important conformational change.
Link to Learning
*
Section Summary
ATP is the primary energy-supplying molecule for living cells. ATP is comprised of a nucleotide, a five-carbon sugar, and three phosphate groups. The bonds that connect the phosphates (phosphoanhydride bonds) have high-energy content. The energy released from ATP hydrolysis into ADP + Pi performs cellular work. Cells use ATP to perform work by coupling ATP hydrolysis’ exergonic reaction with endergonic reactions. ATP donates its phosphate group to another molecule via phosphorylation. The phosphorylated molecule is at a higher-energy state and is less stable than its unphosphorylated form, and this added energy from phosphate allows the molecule to undergo its endergonic reaction.
*
Glossary
- ATP
- adenosine triphosphate, the cell’s energy currency
- phosphoanhydride bond
- bond that connects phosphates in an ATP molecule
-
CC LICENSED CONTENT, SHARED PREVIOUSLY
OpenStax, Biology, Section 6.4 ATP: Adenosine Triphosphate
Provided by: Rice University
Access for free at https://openstax.org/details/books/biology-2e
License: CC-BY 4.0
Adapted By: Sarah Malmquist

