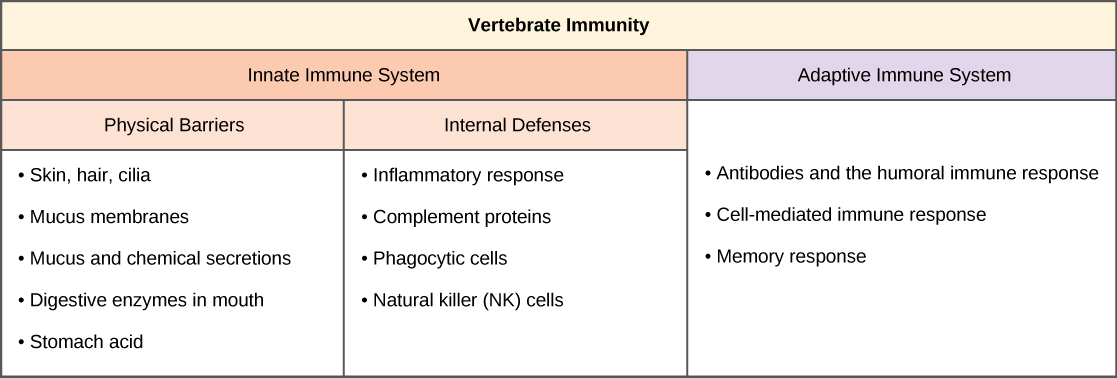
4. Innate Immunity
The immune system in vertebrates, including humans, is a complex multilayered system for defending against external and internal threats to the integrity of the body. Many of these threats are caused by infectious microbes, called pathogens, which include viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites. The system can be divided into two types of defense systems: the innate immune system, which is nonspecific toward a particular kind of pathogen, and the adaptive immune system, which is specific (Figure 1). Innate immunity is not caused by an infection or vaccination and depends initially on physical and chemical barriers that work on all pathogens, sometimes called the first line of defense. The second line of defense of the innate system includes chemical signals that produce inflammation and fever responses as well as mobilizing protective cells and other chemical defenses. Together, the two parts of the innate immune response to a pathogen produce a fast response that is the same every time a pathogen enters the body. This response does not recognize a specific pathogen, but rather recognizes broad patterns of molecules that are not found in healthy human cells or tissues. In contrast, the adaptive immune system mounts a highly specific response to substances and organisms that do not belong in the body, recognizing unique molecular “signatures” found on each pathogen. The adaptive system takes longer to respond and has a memory system that allows it to respond with greater intensity should the body reencounter a the same pathogen again, even years later.
External and Chemical Barriers
The body has significant physical barriers to potential pathogens. The skin contains the protein keratin, which resists physical entry into cells. Other body surfaces, particularly those associated with body openings, are protected by the mucous membranes. The sticky mucus provides a physical trap for pathogens, preventing their movement deeper into the body. The openings of the body, such as the nose and ears, are protected by hairs that catch pathogens, and the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract have cilia that constantly move pathogens trapped in the mucus coat up to the mouth.
The skin and mucous membranes also create a chemical environment that is hostile to many microorganisms. The surface of the skin is acidic, which prevents bacterial growth. Saliva, mucus, and the tears of the eye contain an enzyme that breaks down bacterial cell walls. The stomach secretions create a highly acidic environment, which kills many pathogens entering the digestive system.
Finally, the surface of the body and the lower digestive system have a community of microorganisms such as bacteria, archaea, and fungi that coexist without harming the body. There is evidence that these organisms are highly beneficial to their host, combating disease-causing organisms and outcompeting them for nutritional resources provided by the host body. Despite these defenses, pathogens may enter the body through skin abrasions or punctures, or by collecting on mucosal surfaces in large numbers that overcome the protections of mucus or cilia.
*
Internal Defenses
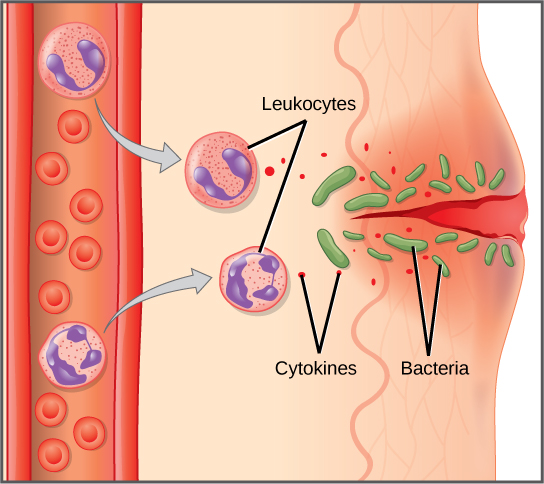
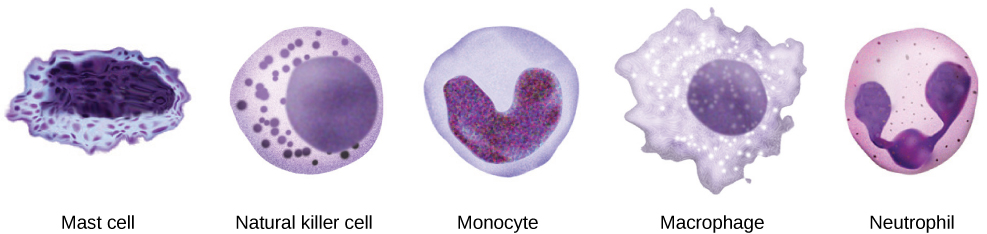
When pathogens enter the body, the innate immune system responds with a variety of internal defenses. These include the inflammatory response, phagocytosis, natural killer cells, and the complement system. White blood cells in the blood and lymph recognize pathogens as foreign to the body, and carry out these defense responses, often with the help of chemical signaling molecules they release. A white blood cell, also called a leukocyte, is larger than a red blood cell, is nucleated, and is typically able to move using amoeboid locomotion. Because they can move on their own, white blood cells can leave the blood to go to infected tissues. For example, a monocyte is a type of white blood cell that circulates in the blood and lymph and develops into a macrophage after it moves into infected tissue. A macrophage is a large cell that engulfs foreign particles and pathogens. Mast cells are produced in the same way as white blood cells, but unlike circulating white blood cells, mast cells take up residence in the tissues other than blood. They are responsible for releasing chemicals in response to physical injury.
When a pathogen is recognized by white blood cells, chemicals called cytokines are released. A cytokine is a chemical messenger that regulates many different cellular processes, including cell division and gene expression, to produce a variety of immune responses. Approximately 40 types of cytokines exist in humans. In addition to being released from white blood cells after pathogen recognition, cytokines are also released by the infected cells and bind to nearby uninfected cells, inducing those cells to release cytokines. This positive feedback loop results in a burst of cytokine production.
One class of early-acting cytokines is the interferons, which are released by infected cells as a warning to nearby uninfected cells. An interferon is a small protein that signals a viral infection to other cells. The interferons stimulate uninfected cells to produce compounds that interfere with viral replication. Interferons also activate macrophages and other cells.
The Inflammatory Response and Phagocytosis
The first cytokines to be produced encourage inflammation, a localized redness, swelling, heat, and pain. Inflammation is a response to physical trauma, such as a cut or a blow, chemical irritation, and infection by pathogens (viruses, bacteria, or fungi). The chemical signals that trigger an inflammatory response enter the extracellular fluid and cause capillaries to dilate (expand) and capillary walls to become more permeable, or leaky. The serum and other compounds leaking from capillaries cause swelling of the area, which in turn causes pain. Various kinds of white blood cells are attracted to the area of inflammation. The types of white blood cells that arrive at an inflamed site depend on the nature of the injury or infecting pathogen. For example, a neutrophil is an early arriving white blood cell that engulfs and digests pathogens. Neutrophils are the most abundant white blood cells of the immune system (Figure 2). Macrophages follow neutrophils and take over the phagocytosis function and are involved in the resolution of an inflamed site, cleaning up cell debris and pathogens. The process of ingesting and digesting up pathogens is called phagocytosis, and the cells that carry this process out are called phagocytes.
Cytokines also send feedback to cells of the nervous system to bring about the overall symptoms of feeling sick, which include lethargy, muscle pain, and nausea. Cytokines also increase the core body temperature, causing a fever. The elevated temperatures of a fever inhibit the growth of pathogens and speed up cellular repair processes. For these reasons, suppression of fevers should be limited to those that are dangerously high.
Concept in Action
Natural Killer Cells
A lymphocyte is a white blood cell that contains a large nucleus (Figure 3). Most lymphocytes are associated with the adaptive immune response, but infected cells are identified and destroyed by natural killer cells, the only lymphocytes of the innate immune system. A natural killer (NK) cell is a lymphocyte that can kill cells infected with viruses (or cancerous cells). NK cells identify intracellular infections, especially from viruses, by the altered expression of particular types of proteins on the surface of infected cells. Unhealthy cells, whether infected or cancerous, display an altered set of proteins on their cell surfaces.
After the NK cell detects an infected or tumor cell, it induces programmed cell death, or apoptosis. Phagocytic cells then come along and digest the cell debris left behind. NK cells are constantly patrolling the body and are an effective mechanism for controlling potential infections and preventing cancer progression. The various types of immune cells are shown in Figure 4.
Complement
An array of approximately 20 types of proteins, called a complement system, is also activated by infection or the activity of the cells of the adaptive immune system and functions to destroy extracellular pathogens. Liver cells and macrophages synthesize inactive forms of complement proteins continuously; these proteins are abundant in the blood serum and are capable of responding immediately to infecting microorganisms. The complement system is so named because it is complementary to the innate and adaptive immune system. Complement proteins bind to the surfaces of microorganisms and are particularly attracted to pathogens that are already tagged by the adaptive immune system. This “tagging” involves the attachment of specific proteins called antibodies (discussed in detail later) to the pathogen. When they attach, the antibodies change shape providing a binding site for one of the complement proteins. After the first few complement proteins bind, a cascade of binding in a specific sequence of proteins follows in which the pathogen rapidly becomes coated in complement proteins.
Complement proteins perform several functions, one of which is to serve as a marker to indicate the presence of a pathogen to phagocytic cells and enhance engulfment. Certain complement proteins can combine to open pores in microbial cell membranes and cause lysis of the cells.
*
Section Summary
The innate immune system consists first of physical and chemical barriers to infection including the skin and mucous membranes and their secretions, ciliated surfaces, and body hairs. The second line of defense is an internal defense system designed to counter pathogenic threats that bypass the physical and chemical barriers of the body. Using a combination of cellular and molecular responses, the innate immune system identifies the nature of a pathogen and responds with inflammation, phagocytosis, cytokine release, destruction by NK cells, or the complement system.
*
Glossary
- complement system
- an array of approximately 20 soluble proteins of the innate immune system that enhance phagocytosis, bore holes in pathogens, and recruit lymphocytes
- cytokine
- a chemical messenger that regulates cell differentiation, proliferation, and gene expression to effect immune responses
- inflammation
- the localized redness, swelling, heat, and pain that results from the movement of leukocytes through opened capillaries to a site of infection
- innate immunity
- an immunity that occurs naturally because of genetic factors or physiology, and is not caused by infection or vaccination
- interferon
- a cytokine that inhibits viral replication
- lymphocyte
- a type of white blood cell that includes natural killer cells of the innate immune system and B and T cells of the adaptive immune system
- macrophage
- a large phagocytic cell that engulfs foreign particles and pathogens
- mast cell
- a leukocyte that produces inflammatory molecules, such as histamine, in response to large pathogens
- monocyte
- a type of white blood cell that circulates in the blood and lymph and differentiates into a macrophage after it moves into infected tissue
- natural killer (NK) cell
- a lymphocyte that can kill cells infected with viruses or tumor cells
- neutrophil
- a phagocytic leukocyte that engulfs and digests pathogens
- phagocytosis
- the process by which a cell engulfs and digests a small object, such as a viral particle, bacterium or piece of cellular debris. Cells that can carry out phagocytosis are called phagocytes.
pathogen
a microbe (virus, bacteria, fungus, parasite) capable of causing disease
- white blood cell
- a nucleated cell found in the blood that is a part of the immune system; also called leukocytes
-
-
-
-
CC LICENSED CONTENT, SHARED PREVIOUSLY
OpenStax, Concepts of Biology, Section 17.2 Innate Immunity
Provided by: Rice University
Access for free at https://openstax.org/details/books/concepts-biology
License: CC-BY 4.0
Adapted By: Sarah Malmquist
-
-
-

